Uses and types of work safety gear
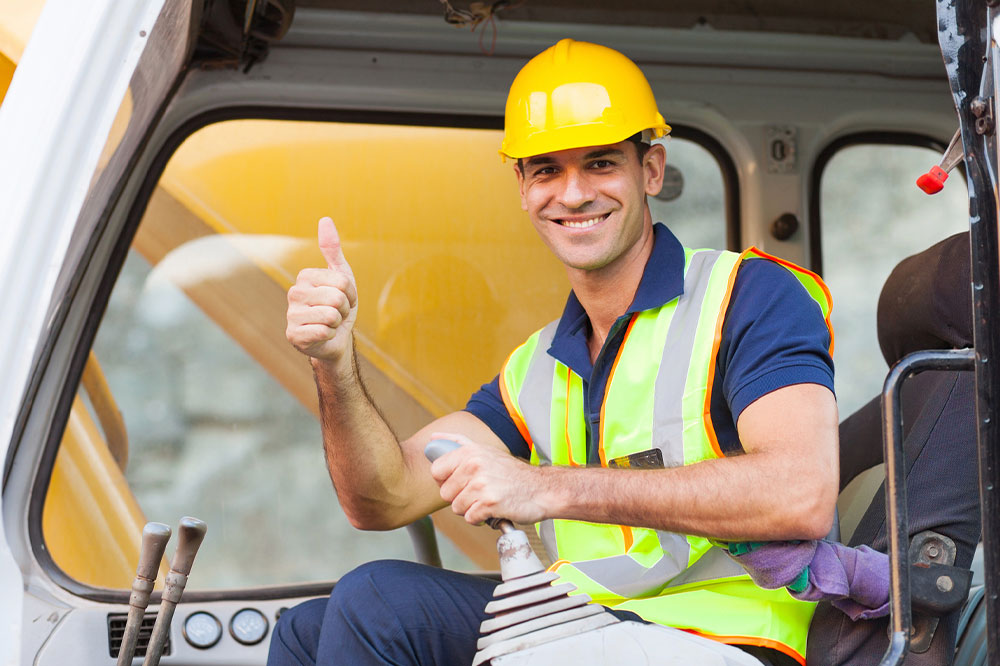
Safety protective gear, also called Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), defends people against workplace accidents, infection, injury, and contamination. It is mainly used in healthcare, mining, construction, transportation, and maritime sectors. Businesses in these industries must use quality protective gear. The Occupation and Safety Health Administration (OSHA) lays down the standards businesses must follow when using such equipment. Read on to learn about the benefits of safety gear and its types.
Uses of safety protective gear
Despite taking the best precautions, accidents can happen in the workplace. The risk of a mishap is manifold in hazardous work settings, such as auto repair shops, mechanical workshops, chemical plants, nuclear plants, thermal plants, and mining sites. Therefore, people in these industries use different types of safety gear to protect themselves from harm. Since strict safety laws govern such industries, businesses cannot become complacent when protecting their workers. The uses of work safety protective gear include:
- Protecting the head from injury due to impact from objects, falls, and bumps.
- Protecting the eyes and face from flying objects, extreme climate, chemicals, dust, and optical radiation.
- Protecting the hands and skin from absorption of hazardous substances, chemicals, heat, fire burns, bruises, cuts, and fractures.
- Protecting the feet and legs from falling objects, sharp tools, slippery surfaces, heat and cold, and exposure to hazardous chemicals.
Types of personal protective equipment
By law, employers in industries like construction and healthcare are required to provide their staff with personal protective equipment. An employer should know what type of PPE their workers need, depending on their jobs. They should also train the employees to use, store, maintain, and dispose of the gear.
PPE kits can be placed into different groups depending on which body part they protect:
- Respiratory: air-purifying filters and masks that protect against contaminated air
- Hearing: ear muffs, ear plugs, and canal caps
- Head: helmets, hard hats, bump caps, and hair nets
- Eyes: safety spectacles, eye shields, safety goggles, and face shields
- Feet and legs: safety boots, wellington boots, and anti-static and conductive footwear
- Hands and arms: gloves, gauntlets, finger guards, and wrist cuff armlets
- Body: aprons, high-visibility jackets, trousers, vests, life jackets, harnesses
Types of safety clothing
People working with toxic materials wear safety clothing over their regular outfits to defend themselves. The protective clothes could be manufactured to resist water, radiation, chemicals, fire, puncture, contamination, electric charge, and other hazards. Examples of safety clothing include:
- Laboratory coats
- Surgical gowns
- Full-body suits
- Chaps pants
- High-visibility vests and pants
- Coveralls
- Gloves
- Aprons
- Boots
- Life jackets
Work safety protective gear aims to protect workers from injury caused by physical, mechanical, electrical, chemical, and other workplace hazards. It protects the eyes, face, feet, hands, ears, head, or whole body, depending on the nature of the job. However, using the gear correctly is vital for it to be effective. Therefore, employers must not only give their staff the right equipment but ensure they know how to use it for their safety. Both employers and employees are responsible for using such gear to create a safe work environment.