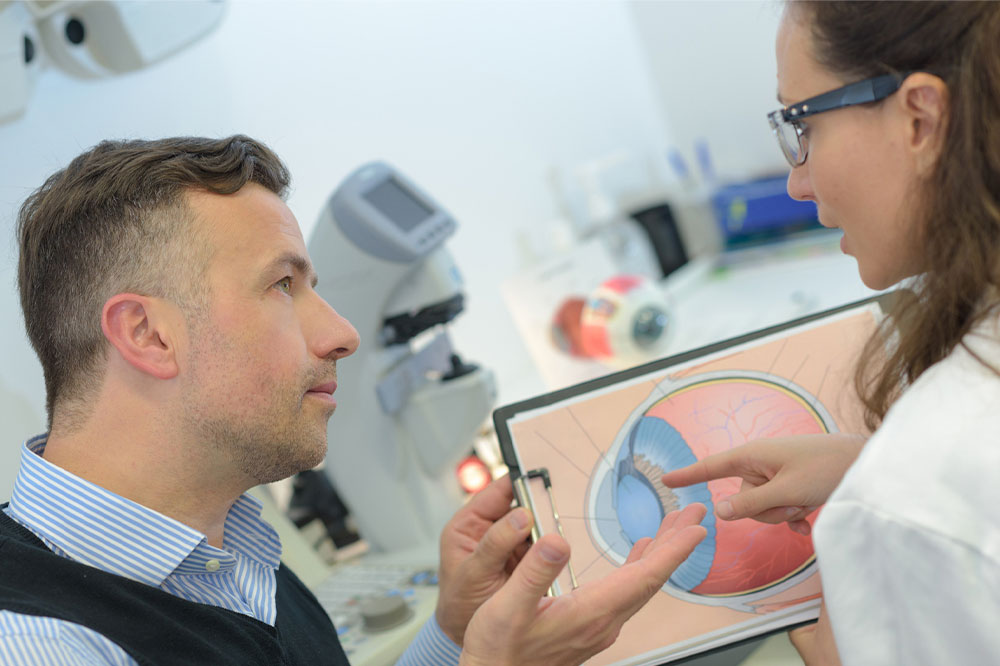
Macular degeneration – Things to know about the condition
Macular degeneration, also called age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is an eye condition that arises when the retina’s center, called the macula, deteriorates. It causes a loss of sight in the central field of vision. People with this eye disease cannot see things clearly in front of them, but their peripheral vision is often normal. Individuals over fifty are more likely to be diagnosed with AMD, and here are a few things one ought to know about the condition:
Types
Macular degeneration is classified into two types:
- Dry AMD: It is also known as atrophic AMD. The condition occurs when the macula thins with age. The precise reason for this is not yet identified.
- Wet AMD: It is also known as exudative AMD. It happens when new blood vessels grow under the retina, and these later leak blood into the macula, scarring it.
Macular degeneration signs and symptoms
The AMD worsens with time, and the manifestations may not be prominent in the early stages. The most common macular degeneration signs and symptoms include the following:
- Blurred vision
- Low vision
- Less visibility in the dim light
- Changes or problems with the way the person sees colors
- Straight lines are seen as wavy or curvy
- Trouble recognizing faces
- Dark spots or blank spots in the field of vision
The signs and symptoms vary with dry and wet types of AMD.
Macular degeneration causes
There is no exact explanation for the cause of macular degeneration. Some of the risk factors involved in its development are briefed below:
- Age over fifty
- Family history of the condition
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Cholesterol problem
- Diabetes
- Infections
- Head injuries
- Meals low in nutrients
Diagnosis and macular degeneration treatment
Ophthalmologists diagnose AMD with the help of various tests such as the following:
- Amsler grid test
- Dilated eye exam
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
- Fluorescein angiography
- OCTA (Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography)
The healthcare provider suggests a macular degeneration treatment plan based on a proper diagnosis. The therapy depends on the type and stage of the condition.
Macular degeneration remedies
Macular degeneration remedies may help slow its progression or prevent this condition from developing in another eye. A combination of vitamins C and E, zinc, beta-carotene, and copper can help manage the disease. However, it is always advisable to have this after discussing it with a physician. The other prevention tips are as follows:
- Exercise regularly and stay physically active.
- Maintain and manage healthy blood pressure.
- Maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods.
The foods that help with macular degeneration are green, leafy vegetables, whole grains, fruits, and healthy fats. For example, corn, broccoli, oranges, strawberries, peas, green peppers, and tomatoes contain lutein and other antioxidants that help reduce the risk of AMD.
Age-related macular degeneration is one of the primary causes of vision loss in older people, and no cure has been devised yet. Checking with an eye care provider is always the best option when one experiences any symptoms. And this post’s purpose is to provide information only. They will provide the right diagnosis and advice to deal with macular degeneration.